You might have heard that vitamins are good for health but today I will be sharing deep information on fat soluble vitamins. Do you know there are 2 basic types of vitamins based on solubility? The fat soluble vitamins and water soluble vitamins. This article will discuss fat soluble vitamins in the article below.
This Article Contains
Fat Soluble Vitamins Definition
Fat-soluble vitamins are the ones that are having solubility in fats. These are the kind of vitamins that are absorbed with oils and fats and stored in the liver and the body’s fatty tissues. They are found in many plant and animal foods and fat soluble dietary supplements. Vitamins A, D, E, and K are known as fat soluble vitamins.
Fat Soluble Vitamins Includes
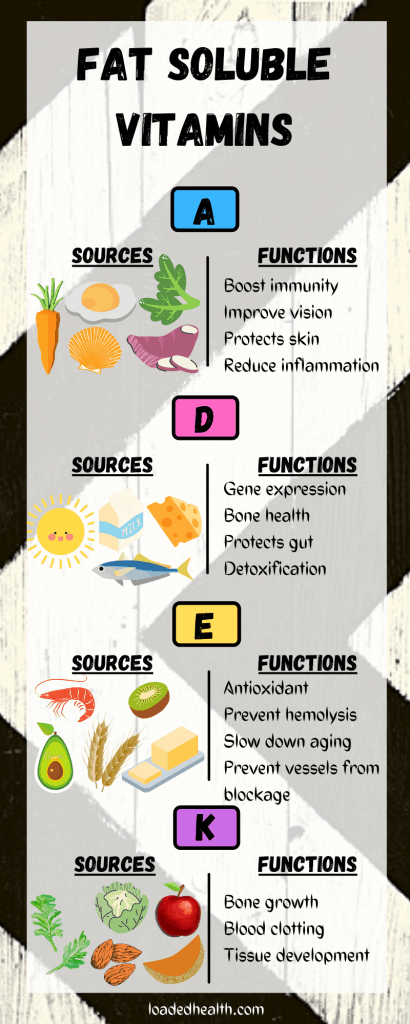
- VITAMIN A
- VITAMIN D
- VITAMIN E
- VITAMIN K
FAT-SOLUBLE VITAMINS PDF
Fat-Soluble Vitamins Functions
VITAMIN A
Here are some important functions of Vitamin A:
- Crucial for maintaining vision.
- Promote growth and development.
- Protect skin and maintain integrity in the body.
- Having anti-inflammatory properties.
- Enhance your immune function.
- Involved in the development of the immune system.
- Involved In the normal metabolism of bones.
- Having many other cellular level benefits in the body.
VITAMIN D
Here are some important functions of Vitamin D:
- Involved in the maintenance of healthy bones and teeth.
- Vitamin D is involved in the regulation and absorption of Ca2+ and phosphate.
- It also controls gene expression or code.
- Supports normal function of the immune system.
- Help in detoxification of your body via antioxidants.
- Good for gut health.
- Enhance skin growth.
- Effective against COVID-19. See Supplements for COVID-19.
VITAMIN E
Here are some important functions of Vitamin E:
- Most powerful natural antioxidant.
- Protects hemolysis that is a breakdown of red blood cells.
- Early aging.
- Boosts immune response.
- Blockage of blood vessels.
VITAMIN K
Here are some important functions of Vitamin K:
- Helps in blood clotting.
- Bone growth.
- Tissue development.
Fat Soluble Vitamins Deficiency
VITAMIN A
The deficiency of Vitamin A can cause:
- Dry eyes.
- Dryness in the skin.
- Poor skin health and sebum production.
- Delayed healing of wounds.
- Impaired immune system.
- Delayed growth.
- Recurrent infections.
- Delayed growth.
- Difficulties in conceiving.
VITAMIN D
The deficiency of Vitamin D:
- Inflammation.
- Excess fatigue.
- Heart health will be compromised.
- Bone health will be compromised.
- Depression and mood swings.
- Inability to fight infections efficiently.
- Increase cancer risk.
- Poor muscle strength, weak muscles, cramps/pain in muscles.
- Improper cell growth.
- Some disease includes Rickets, Osteoporosis, and Osteomalacia.
VITAMIN E
The deficiency of Vitamin E can cause:
- Anemia.
- Increased risks of cancer.
- Muscular cramps.
- Skin dryness.
- Compromised skin and hair health.
- Immune impairment.
- Can affect eyesight.
- Weakness in muscles and joints.
VITAMIN K
The deficiency of Vitamin K can cause:
- Easy bruising.
- Bleeding in urine.
- Difficulty in stopping the bleeding.
- Excessive bleeding after trauma, surgery, and from wounds/cuts.
- Heavy periods.
- Bleeding from internal organs such as the stomach, intestine, or rectum.
- Gum or nose bleed.
Recommended Daily Intake of Fat Soluble Vitamins
VITAMIN A
This is the RDA of Vitamin A:
- Children = 400–600 mcg/day.
- Men = 750–1000 mcg/day.
- Women = 700 mcg/day.
- Pregnancy = 750 – 770 mcg/day.
- Lactation = 1200 – 1300 mcg/day.
VITAMIN D
This is the RDA of Vitamin D:
- 0-12 months = 10 mcg/day.
- 1-70 years = 15 mcg/day.
- >70 years = 20mcg/day.
- Lactating = 15 mcg/day.
- Pregnant = 15 mcg/day.
VITAMIN E
This is the RDA of Vitamin E:
- Children = 5-11 mg/day.
- Males = 15 mg/day.
- Females = 15 mg/day.
- Pregnancy = 15 mg/day.
- Lactation = 19 mg/day.
VITAMIN K
This is the RDA of Vitamin K:
- 0–6 months = 2mcg/day.
- 7–11months = 2.5 mcg/day.
- 1–3years = 30 mcg/day.
- 4–13years = 55 – 60 mcg/day.
- 14–18years = 75 mcg/day.
- Female = 90 mcg/day.
- Male = 120 mcg/day.
- Pregnancy = 75 – 90 mcg/day.
- Lactation = 75 – 90 mcg/day.
Additional Information On Vitamin A
TYPES
There are 4 types of Vitamin A and its derivatives based on structure:
- Vitamin A-Ester.
- Vitamin A-1.
- Vitamin A-Aldehyde.
- Vitamin A-Saure.
DIETARY SOURCES
Vitamin A has many dietary sources namely:
- Carrot
- Red meats.
- Chicken.
- Fish and shellfish.
- Eggs.
- Milk.
- Legumes and seeds.
- Green vegetables.
- Yellow vegetables.
- Sweet potatoes.
- Yellow fruits.
- Red palm oil.
- Other vegetable oils.
TOXICITY
Excessive intake of Vitamin A causes toxicity.
- Anorexia
- Irritability
- Rash
- Headache
- Loss of hair.
- Peeling of skin
- Drowsiness and vomiting
- Bad effects on the liver cause cirrhotic liver and portal hypertension.
Additional Information On Vitamin D
TYPES
Vitamin D mainly of 2 types:
- Ergocalciferol (D2).
- Cholecalciferol (D3).
DIETARY SOURCES
Some of the dietary sources of Vitamin D are:
- Fatty fish.
- Eggs especially yolk.
- Cereals.
- Liver and liver oils.
- Milk.
- Beef, Mutton.
- Papaya.
- Yogurt.
- Cheese.
- Mushrooms.
TOXICITY
The excess amounts of Vitamin D consumption can cause:
- Brain damage (cerebral).
- Kidney damage.
- Heart damage.
Additional Information On Vitamin E
TYPES
Vitamin E is mainly of 2 types:
- Tocopherol.
- Tocotrienol.
DIETARY SOURCES
Here are some dietary sources of Vitamin E:
- Seeds and nuts.
- Kiwi
- Spanish.
- Avacado.
- Squash.
- Broccoli.
- Shrimp.
- Olive oil.
- Wheat.
- Tomatoes.
- Apricots.
- Margarine.
TOXICITY
The excess of Vitamin E can cause:
- Severe skin allergies.
Additional Information On Vitamin K
TYPES
There are 3 types of Vitamin K mainly:
- K-1.
- K-2.
- K-3.
DIETARY SOURCES
Here are some dietary sources of Vitamin K:
- Melon.
- Apples.
- Grapes.
- Brocolli.
- Nuts and seeds.
- Kale.
- Cabbage.
- Lettuce.
- Pulses.
- Avocado.
TOXICITY
The toxicity of Vitamin K especially Vitamin K1 can cause:
- Excessive blood loss – hemorrhage.
FAQs On Fat Soluble Vitamins
What Are Fat Soluble Vitamins and What Does This Mean?
There are in total 4 fat soluble vitamins. These are the types of vitamins that will be needing oils and oil preparation to get dissolved and function.
What Is The Function of Fat Soluble Vitamins?
Fat soluble vitamins have several different functions and they vary on the Vitamin type. Follow the post above for details.
Is Vitamin C Fat Soluble?
No, Vitamin C is not a fat soluble vitamin instead it is a water-soluble vitamin.
Do Fat Soluble Vitamins Make You Gain Weight?
No, fat-soluble vitamins as its name suggests are completely different from them. They don’t contribute to increasing the fats in your body or gain weight.
Do You Need To Eat Fats To Absorb Fat Soluble Vitamins?
Not necessarily but as these fat soluble vitamins A, D, E, K absorbs in fat tissues. So, yes if consumed with fats the absorption will be higher and better.
Which Fat Soluble Vitamin Is a Hormone?
Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin which is a hormone used to absorb and regulate calcium and phosphate in the blood.
Fat Soluble Vitamins Video
Summarizing The Fat Soluble Vitamins
So, that is all about your complete guide on fat soluble vitamins. I have summarized this for your better understanding. These fat soluble vitamins are important to keep your vital organs function. Try to consume them within the recommended daily allowance as mentioned to keep their level to optimum.
Follow Loaded Health for more discussions on nutrition, health, and fitness.







